The three commercially available GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulators (CGP7930, GS39783 and rac-BHFF) have been used widely in animals and in vitro. Here using whole cell electrophysiology, we compared the potentiation of GABAB receptor activated K+ currents in HEK cells and hippocampal neurons.
rac-BHFF is the most efficacious PAM followed by GS39783 and CGP7930
In HEK-293 cells and hippocampal neurons, rac-BHFF is the most efficacious PAM followed by GS39783

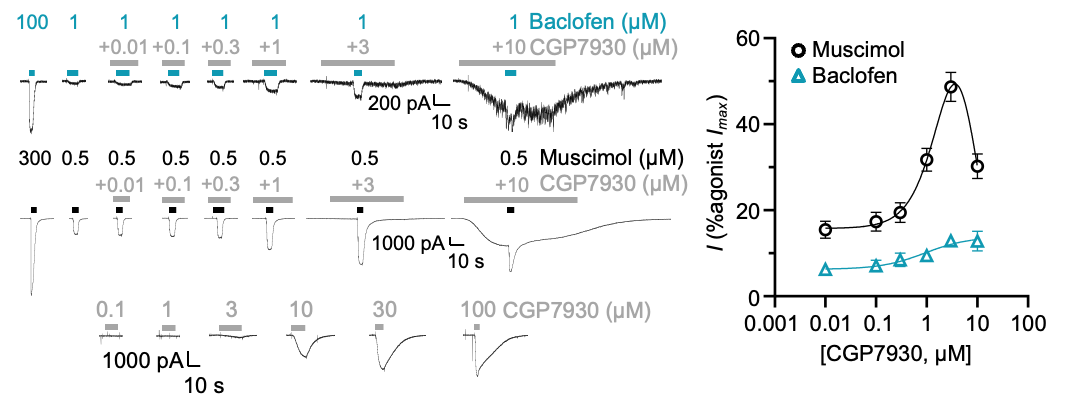
CGP7930 is a GABAA receptor and K+ channel modulator
CGP7930 potentiated GABAA receptor currents in neurons and HEK-293 cells. At high concentrations, CGP7930 directly activates GABAA receptors and proceeds to inhibit these ion channels as concentration is increased.
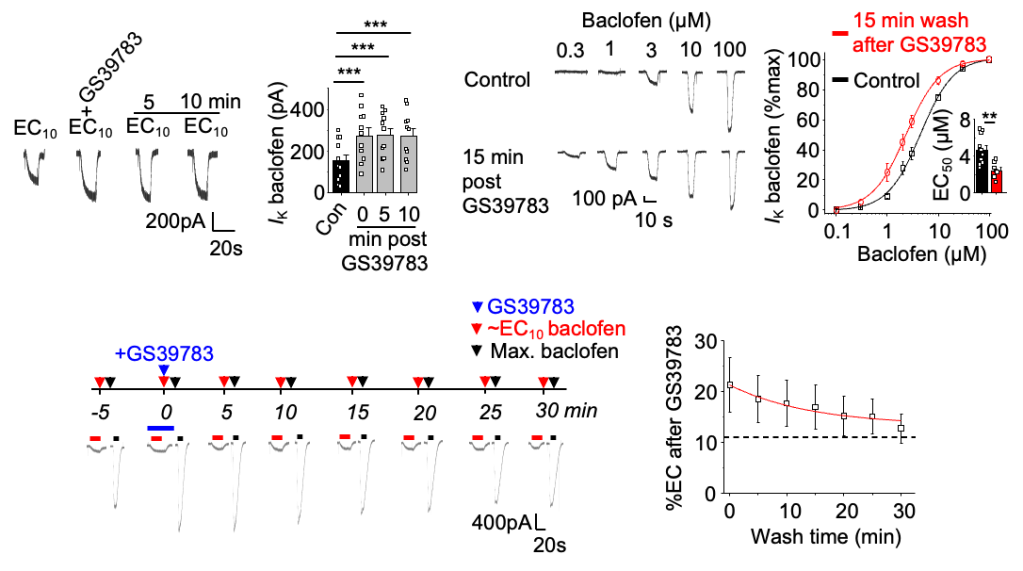
GS39783 does not wash off from GABAB receptors even after prolonged washes
In hippocampal neurons GS39783 was slow to wash-off with potentiated baclofen responses following a single 3 μM sub-maximal GS39783 exposure reduced by only ~5% after 10 min of wash. The baclofen EC50 post-GS39783 remained lower even after 15 min wash compared to the control pre-GS39783 EC50.
Intriguingly, the recovery kinetics for GS39783 potentiation during the wash-off phase, studied in GIRK cells by applying consecutive pairs of ~EC10 and maximal baclofen concentrations every 5 min following a single exposure to 3 μM GS39783, is similar to the rate of internalization for cell surface GABABRs in the same cells.
This similarity may imply that GS39783 binds tightly to the GABABR and that potentiation is only terminated predominantly via endocytosis instead of PAM unbinding.
For more details please visit the publications:
*corresponding authors