In this study, while characterising GABAA receptor variants of a predominant receptor subtype, we discovered that spontaneous GABAA receptor mutations can counterintuitively underlie seizures. We were able to reverse some of the phenotypic anomalies by using a naturally produced inhibitory neurosteroid with important implications for therapy of this emerging class of genetic epilepsies.
Altered structural plasticity of dendritic spines due to spontaneously active variants
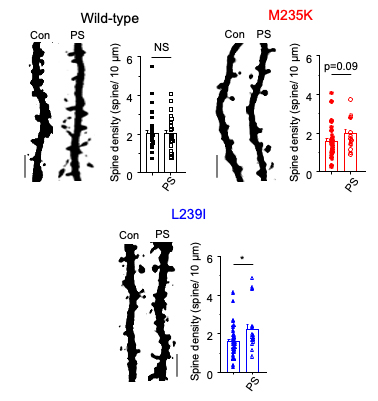
Expression of M263K (M235K without signal sequence) and L267I (L239I without signal sequence) in hippocampal neurons resulted in reduced dendritic spine density and percentage of mature or mushroom spines with a concomitant increase of percentage of thin or immature spines.

An inhibitory neurosteroid reverses deficits in dendritic spine plasticity
Application of a naturally occurring, inhibitory neurosteroid pregnenolone sulphate normalised dendritic spine defects for L239I. For M235K, spine density showed a tendency to increase in pregnenolone sulphate compared to untreated M253K-expressing cells.
For more details please visit the publication:
*corresponding authors