Here we reveal that protein kinase A phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 affects inhibitory neurotransmission by modulating synaptic concentrations of the adhesion protein.
The trans-synaptic adhesion molecule neuroligin-2 (NL2) is essential for the development and function of inhibitory synapses. In collaboration with Dr Els Hallf and Professor Josef Kittler (UCL, London, UK) we show that post-translational modification dynamically alters synaptic levels of neuroligin-2 with important consequences for inhibitory neurotransmission.
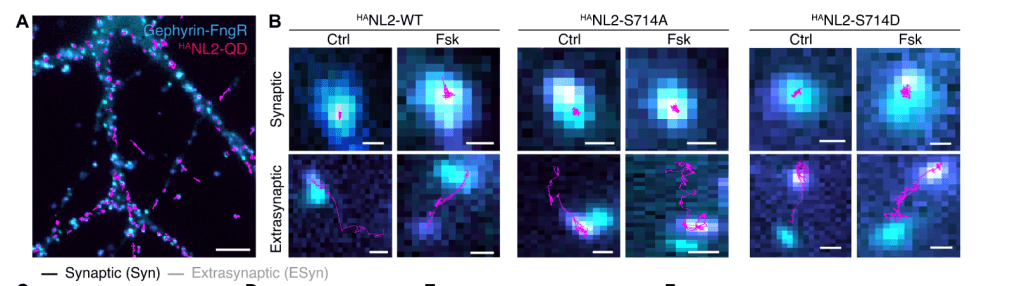
Phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 at Ser714 causes its synaptic dispersion
Using single particle tracking of quantum dot labelled neuroligin-2, we show that phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 at Ser714 causes its dispersal from inhibitory synapses.
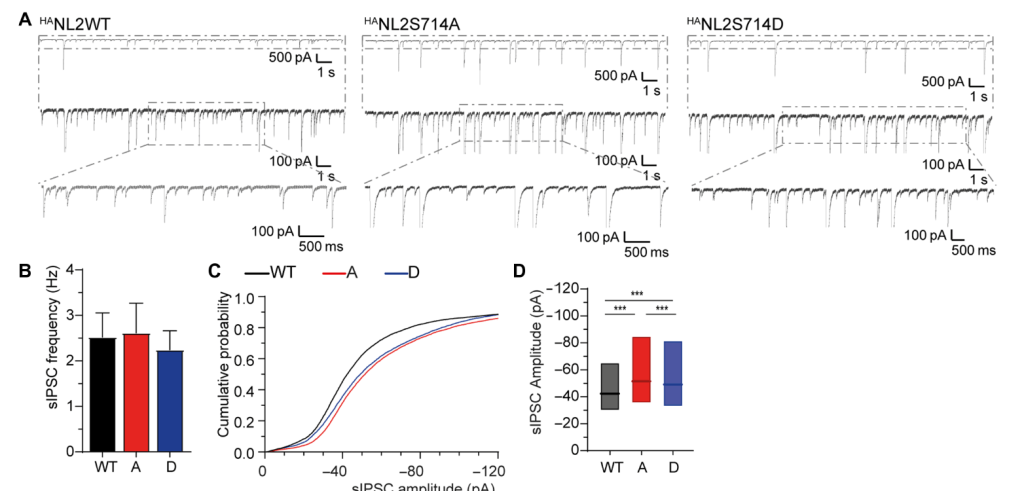
Phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 at Ser714 affects inhibitory signaling
Using whole cell electrophysiology, we show that phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 affects the efficacy of GABAergic neurotransmission.